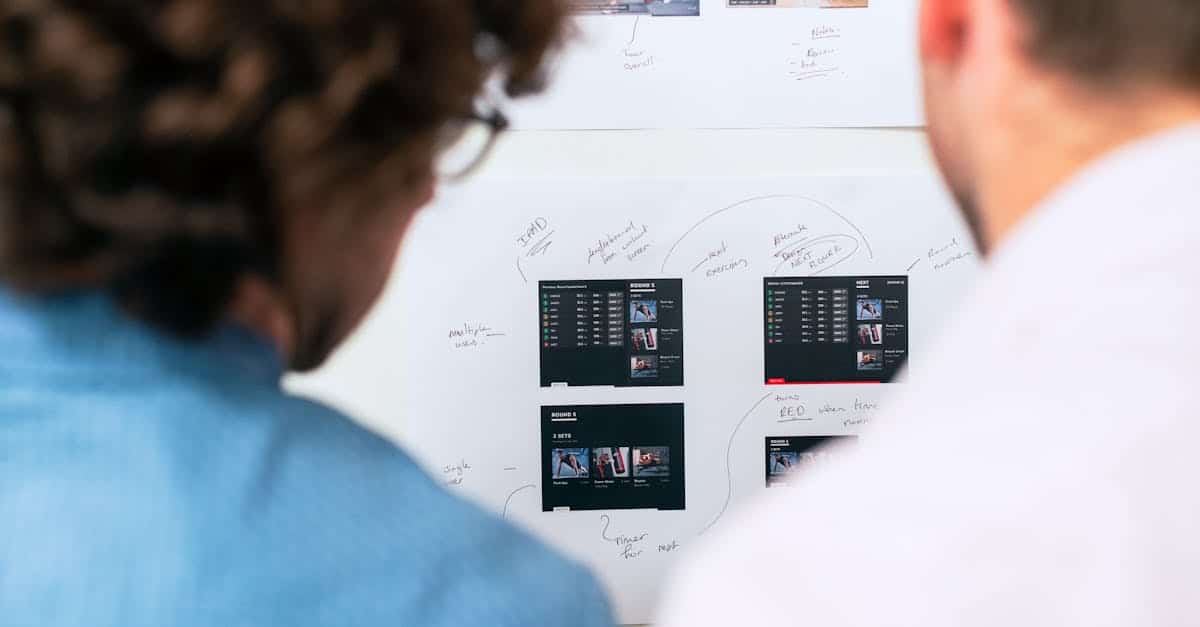
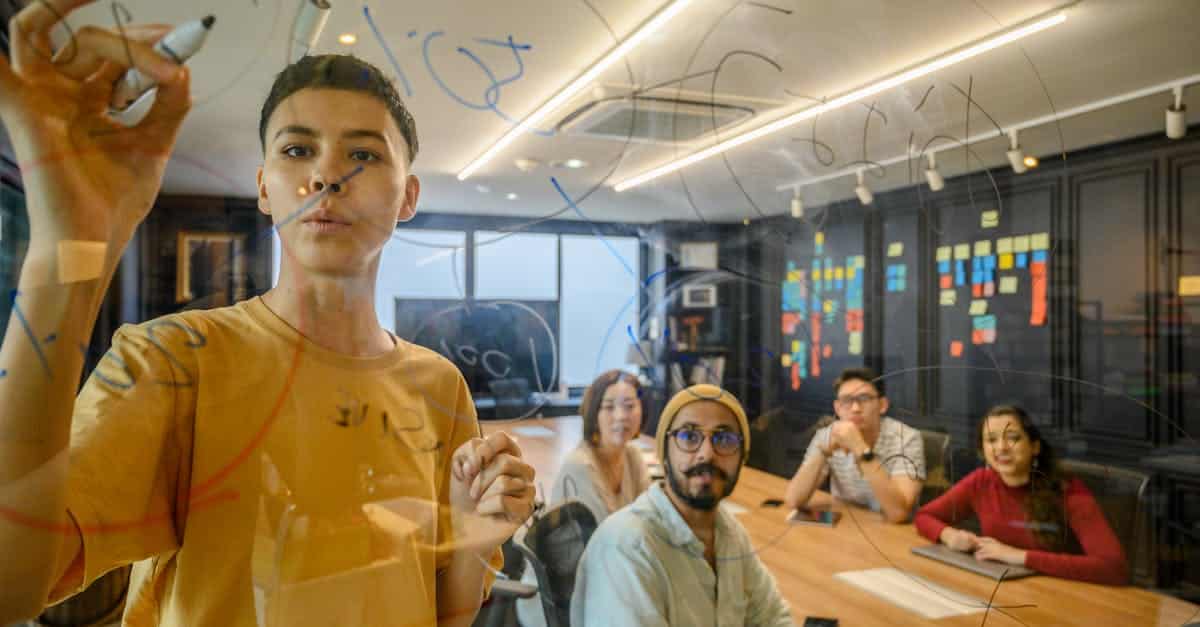
Design thinking has emerged as an essential method for problem solving and innovation within organizations. By placing the user at the heart of concerns, this approach allows for a better understanding of the real needs of consumers while fostering creativity through sustainable solutions. The capacity to deconstruct complex problems and reinvent them makes design thinking particularly relevant in a constantly evolving economic context. Through an iterative process, it encourages experimentation and the adoption of new perspectives, thus bringing real dynamism to teams.

Design thinking is a methodology that is gaining more and more traction across various sectors, particularly in innovation, product development, and the resolution of complex problems. Its essence lies in a human-centered approach, allowing for a deep and meaningful understanding of user needs, aspirations, and behaviors.
At the heart of design thinking is the understanding of users. By placing them at the center of the creation process, it becomes possible to identify real needs that might be overlooked by traditional methods. This approach fosters better empathy between designers and users, enabling the formulation of solutions that are not only functional but also desirable. This is even more relevant in a world where consumers are increasingly demanding and informed.
Moreover, design thinking is characterized by its iterative and non-linear process. Unlike traditional analytical methods that proceed according to a rigid schema, this methodology generates a continuous cycle of testing, evaluating, and adjusting. Each step aims to challenge pre-established assumptions, thus fostering a culture of innovation within teams. For example, by developing prototypes, teams can gather feedback directly from users, refining their understanding and improving their solutions.
Another essential dimension of design thinking is its ability to stimulate creativity. By creating an environment where ideas are shared freely and where failure is viewed as an opportunity for learning, design thinking fosters interdisciplinary collaboration. Teams are encouraged to explore a variety of solutions and to think outside the box. Thus, a diversity of perspectives enriches the creative process, leading to ideas that can truly transform challenges into opportunities.
Furthermore, design thinking stands out for its ability to be applied in different contexts—whether in education, healthcare, public services, or product and service innovation. Each field can benefit from this methodology to solve problems and create value. For instance, in the healthcare sector, design thinking can help enhance the patient experience by developing services that take into account their specific needs and expectations.
A significant advantage of design thinking is also its potential to reduce risks associated with innovation. By testing ideas on a small sample of users before a large-scale deployment, companies can identify potential issues early and adjust their offerings accordingly. This not only saves resources but also increases the chances of success for new initiatives.
Finally, in a constantly evolving economic context, companies must adapt quickly to changes and new consumer expectations. The flexibility and responsiveness guaranteed by design thinking make it a valuable tool to remain competitive. By adopting this approach, companies do not merely follow trends; they position themselves as innovators, capable of proactively responding to market challenges.

Q: Why is design thinking crucial for businesses? It allows businesses to develop products and services that truly meet consumer expectations, thus fostering innovation and competitiveness in the market.
Q: What are the stages of design thinking? The process generally includes five stages: empathy (understanding needs), definition (redefining issues), ideation (generating ideas), prototyping (creating tangible solutions), and testing (evaluating and refining solutions).
Q: How does design thinking stimulate creativity? This approach encourages the exploration of ideas without fear of failure, allowing for innovation and experimentation with original solutions.
Q: What are the benefits of a design thinking process? Benefits include a better understanding of users, improved products, and an increased ability to respond to changing customer needs.
Q: Does design thinking have limitations? While effective, it is important to recognize that design thinking requires time and resources, and should be used in conjunction with other approaches to be fully effective.
Q: What is the best way to implement design thinking? For successful implementation, it is crucial to involve all stakeholders, maintain an open-minded attitude, and adopt a mindset of collaboration and experimentation.