In our daily interactions, the words we choose can leave a significant mark. Some common expressions, although often employed unconsciously, contribute to the stigma of personality. These words can transform an individual characteristic into a stigma, thereby reinforcing prejudices and stereotypes. When we carelessly use terms like “schizophrenic” or “bipolar” to describe innocuous behaviors, we help to increase discriminatory barriers. Adopting more conscious language is essential to create an inclusive environment that respects differences.

The stigma of personality manifests through the use of frequent expressions that reinforce negative prejudices or stereotypes towards individuals or specific groups. These expressions become tools of disguised discrimination, often acclaiming character traits perceived as deficient or abnormal.
Terms like “schizophrenic” or “bipolar” are commonly used lightly in everyday language to describe unpredictable or contradictory behaviors. Such expressions trivialize the reality of mental disorders and fuel the perception that affected individuals are fundamentally flawed.
Another stigmatizing expression that is on the rise in certain cultural contexts, such as “Are you a T?” in South Korea, exacerbates contempt and isolates individuals due to their peculiarities. Beyond these examples, these formulas often reveal an ignorance of the underlying personal realities and can multi-dimensionally impact the lives of those who are victims of them.
By resisting the use of these expressions, we actively participate in the fight against stigma. It is essential to cultivate inclusive language that values diversity and respects individual differences, contributing to establishing a fairer and more supportive community.
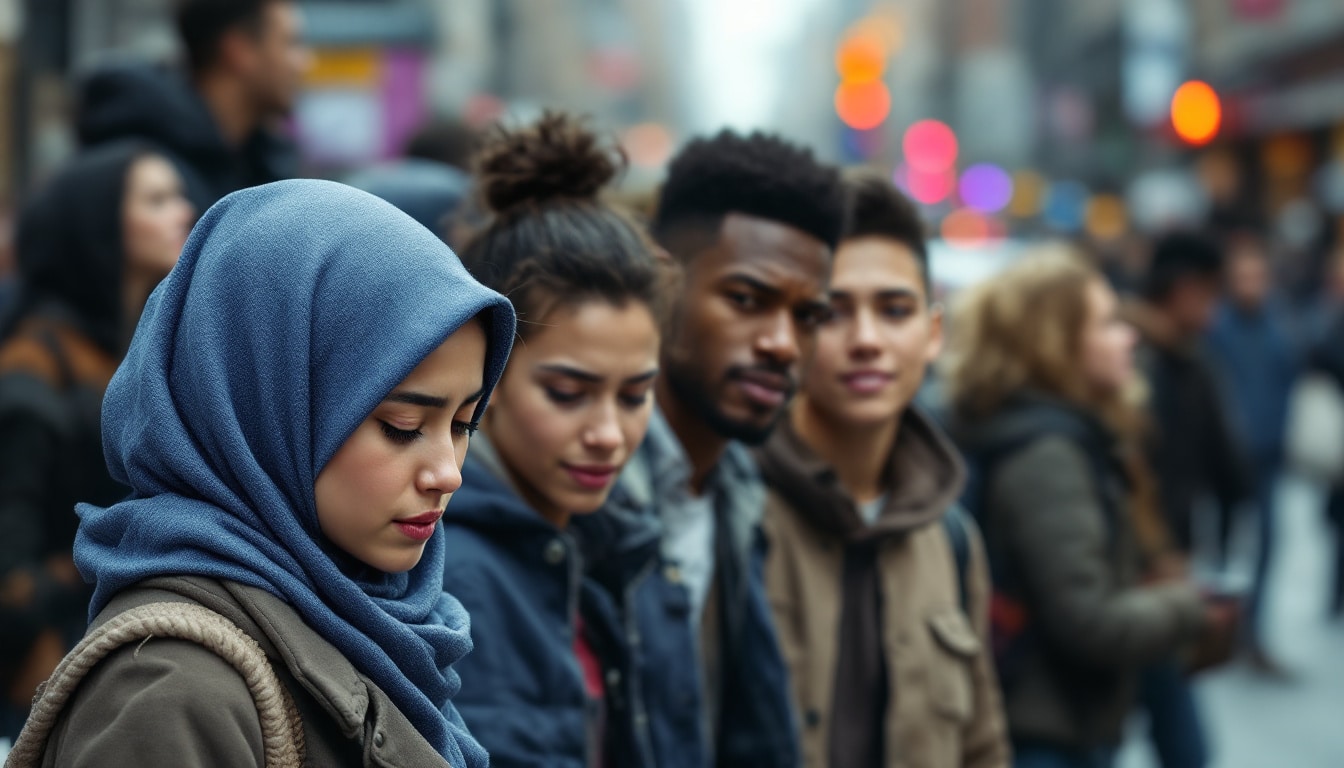

origin of verbal stigmatizations
Language expressions often play a crucial role in how social groups are perceived. The simple choice of words can reinforce stereotypes that shape public mentalities. A common example is the use of psychiatric terms like “schizophrenic” or “bipolar” to designate unpredictable or irrational behavior, thus reducing a person’s individuality to a complex mental situation. This lack of nuance can lead to daily discrimination. The influence of words does not stop there, as even familiar expressions can incorporate implicit biases.
Media, social networks, and daily conversations are rife with expressions that encapsulate archaic prejudices, hidden behind ordinary linguistic fabric. For example, the phrase “Are you a T?” in South Korea has emerged as a new form of disdain (see more in the article here), highlighting how a simple addition to everyday language can transform into an effective and harmful tool of social stigma.
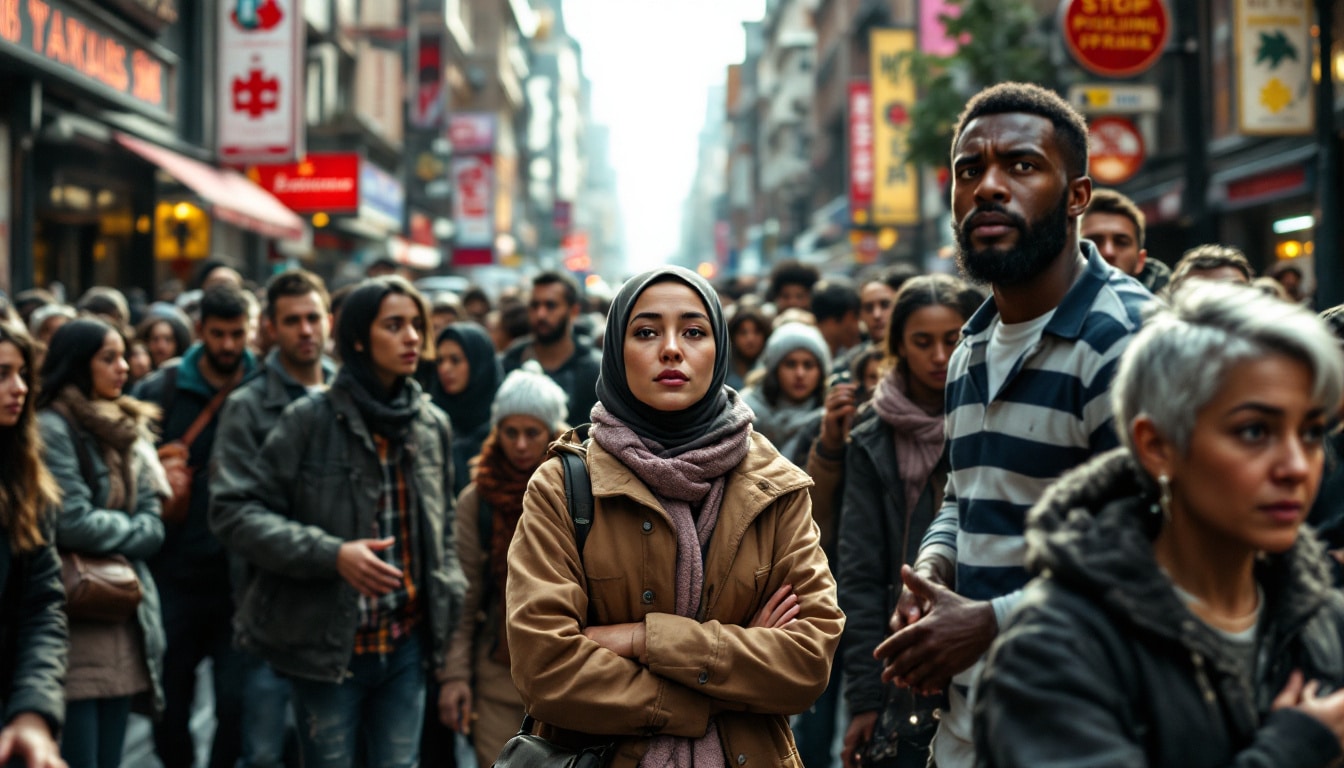
social and individual consequences
An insidious linguistic stigma quietly enters daily life without much attention. Its repercussions affect several spheres of social and personal life. Individuals burdened with stigmas often see their self-esteem severely affected, as the accumulation of prejudices turns into a heavy psychological load. This can lead to a vicious cycle, where stress and anxiety amplify personal crises or mental health issues. Furthermore, this unnoticed stigma can extend in terms of discrimination in vital aspects such as access to care or job searching.
how to educate to stop stigma
It is becoming increasingly urgent to develop educational strategies that proactively confront linguistic stigma. Drawing inspiration from the success of the Cambodian program for combating HIV/AIDS, which has successfully established itself through innovation, efforts can focus on developing a collective discourse where each expression is chosen carefully. Education around everyday words can foster a collective awareness that questions the implicit normalization of these terms. By restoring rights to terms that value rather than reduce, stereotypes can be gradually deconstructed, paving the way for fairer social relations.

FAQ
Q: What is personality stigma?
A: Personality stigma refers to the process by which supposed traits of a person or group are perceived negatively, leading to labeling them in a pejorative manner.
Q: Why are some expressions considered stigmatizing?
A: Some expressions are considered stigmatizing because they are based on stereotypes and prejudices, which reinforce discrimination and elevate these traits to negative symbols.
Q: What consequences can stigma have?
A: Stigma can lead to discrimination, reducing access to care, increasing personal and professional failures, and severely affecting the self-esteem of the individuals concerned.
Q: How can society fight against stigma?
A: The fight against stigma involves education, raising awareness about stereotypes, and supporting affected individuals by encouraging them to speak to relatives or professionals.
Q: What is the role of associations in the fight against stigma?
A: Associations play a crucial role by listening, advising, and helping individuals victimized by stigma to navigate this process and find solutions suited to their personal situations.
Q: Why can psychiatric terms be used stigmatizingly?
A: Psychiatric terms like “schizophrenic” or “autistic” are sometimes misused as insults, contributing to the stigma of mental health conditions and reinforcing erroneous and contemptuous notions.